定时器
定时器作用很多,常见于心跳检测,冷却等等 实现时区别主要在于定时器队列的管控(排序)
基本方案:
红黑树:
使用红黑树对定时器排序,排序依据为定时器过期时间,每隔单位时间检查红黑树中最小时间是否小于等于当前时间,如果小于等于就删除节点并触发节点的callback。时间复杂度增删O(logn),Nginx使用红黑树。删除添加操作自旋。
最小堆:
最小堆根节点最小,直接拿出根节点与当前时间比较即可,删除操作将根节点与末尾节点对换并删除末尾节点然后将新的根节点下沉,添加时加入末尾节点并上升。
时间轮:
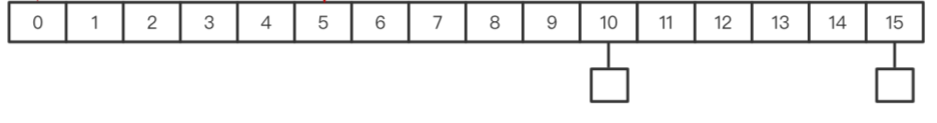
时间轮可以分为单层级与多层级。简单的单层级时间轮使用初始化好的链表数组来存储对应的事件节点链表,时间数据结构中一般包含引用计数,该数据结构只有在引用计数置零后销毁,一般也代表着事件对应的资源可以释放。单层时间轮的大小至少需要大于最长定时时间/单位时间,举例:每5秒发送一个心跳包,连接收到心跳包时需要开启一个10秒的定时器并将事件引用计数加一(事件数据结构插入链表数组中10秒后的链表中),也就是最长定时10秒,10秒后检查该连接对应的事件并将引用计数减一,如果减一后为0就说明连接超时,释放所有资源,关闭事件。在该例子中,初始化的链表数组大小至少为11,因为假如在第0秒来一个心跳包,我们就需要在第10号位置将该连接对应的事件节点加入事件链表中,如果小于11,比如为8,那从0开始往后10个的位置就是在2号位置,那2秒后就得触发了,这与我们设置的10秒定时时间不一致。
代码实现:
红黑树:
红黑树数据结构直接使用nginx自带的rbtree头文件,就不自己写了
红黑树定时器头文件:
#ifndef _MARK_RBT_
#define _MARK_RBT_
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#if defined(__APPLE__)
#include <AvailabilityMacros.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <mach/task.h>
#include <mach/mach.h>
#else
#include <time.h>
#endif
#include "rbtree.h"
ngx_rbtree_t timer;
static ngx_rbtree_node_t sentinel;
typedef struct timer_entry_s timer_entry_t;
typedef void (*timer_handler_pt)(timer_entry_t *ev);
struct timer_entry_s {
ngx_rbtree_node_t timer;
timer_handler_pt handler;
};
static uint32_t
current_time() {
uint32_t t;
#if !defined(__APPLE__) || defined(AVAILABLE_MAC_OS_X_VERSION_10_12_AND_LATER)
struct timespec ti;
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &ti);
t = (uint32_t)ti.tv_sec * 1000;
t += ti.tv_nsec / 1000000;
#else
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
t = (uint32_t)tv.tv_sec * 1000;
t += tv.tv_usec / 1000;
#endif
return t;
}
int init_timer() {
ngx_rbtree_init(&timer, &sentinel, ngx_rbtree_insert_timer_value);
return 0;
}
void add_timer(timer_entry_t *te, uint32_t msec) {
msec += current_time();
printf("add_timer expire at msec = %u\n", msec);
te->timer.key = msec;
ngx_rbtree_insert(&timer, &te->timer);
}
void del_timer(timer_entry_t *te) {
ngx_rbtree_delete(&timer, &te->timer);
}
void expire_timer() {
timer_entry_t *te;
ngx_rbtree_node_t *sentinel, *root, *node;
sentinel = timer.sentinel;
uint32_t now = current_time();
for (;;) {
root = timer.root;
if (root == sentinel) break;
node = ngx_rbtree_min(root, sentinel);
if (node->key > now) break;
printf("touch timer expire time=%u, now = %u\n", node->key, now);
te = (timer_entry_t *) ((char *) node - offsetof(timer_entry_t, timer));
te->handler(te);
ngx_rbtree_delete(&timer, &te->timer);
free(te);
}
}
#endif
expire_timer() 检查红黑树中是否有过期定时器,清理所有过期定时器并触发对应的回调函数
add_timer 向红黑树中插入事件,使用nginx定时器专用的红黑树插入函数,这里红黑树使用黑色哨兵sentinel,其含义如下:
红黑树有一个性质是:
叶结点的左右两边必须为黑色。也就是本来叶结点如果没有左右孩子直接初始化为NULL就是了,但它居然要黑色,意味着我需要新分配两块内存空间啥数据也不保存,tm就是为了给它涂上黑色然后挂到叶结点的left、right。
当叶结点多起来的时候你说多浪费内存空间?理想的二叉树结构是为了让我们保存数据(key),而不是为了保存颜色吧?
所以哨兵这个外援就来了,我们申请一块内存命名为哨兵,然后把这块内存涂上黑色,之后所有没有孩子的叶结点left、right都指向这个已涂上黑色的哨兵。以上是红黑树哨兵的作用。
其他函数较简单
红黑树定时器主文件:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "rbt-timer.h"
void print_hello(timer_entry_t *te) {
printf("hello world time = %u\n", te->timer.key);
}
int main()
{
init_timer();
timer_entry_t *te = malloc(sizeof(timer_entry_t));
memset(te, 0, sizeof(timer_entry_t));
te->handler = print_hello;
add_timer(te, 3000);
for (;;) {
expire_timer();
usleep(10000);
}
return 0;
}
主函数中主事件循环使用单位10秒usleep(10000),usleep中参数单位为ms
最小堆:
最小堆定时器头文件:
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
typedef void (*TimerHandler) (struct TimerNode *node);
struct TimerNode {
int idx = 0;
int id = 0;
unsigned int expire = 0;
TimerHandler cb = NULL;
};
class MinHeapTimer {
public:
MinHeapTimer() {
_heap.clear();
_map.clear();
}
static inline int Count() {
return ++_count;
}
int AddTimer(uint32_t expire, TimerHandler cb);
bool DelTimer(int id);
void ExpireTimer();
private:
inline bool _lessThan(int lhs, int rhs) {
return _heap[lhs]->expire < _heap[rhs]->expire;
}
bool _shiftDown(int pos);
void _shiftUp(int pos);
void _delNode(TimerNode *node);
private:
vector<TimerNode*> _heap;
map<int, TimerNode*> _map;
static int _count;
};
int MinHeapTimer::_count = 0;
需要分析的是struct TimerNode这个数据结构,idx指示在最小堆数组中的位置,用于在定时器过期时确认位置,id用于与_map协作以快速定位并删除特定id的节点,id的值自增长,expire为定时长度,cd是回调函数,具体可以看代码。
最小堆定时器主文件:
#include <unistd.h>
#if defined(__APPLE__)
#include <AvailabilityMacros.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <mach/task.h>
#include <mach/mach.h>
#else
#include <time.h>
#endif
#include <iostream>
#include "minheap.h"
static uint32_t
current_time() {
uint32_t t;
#if !defined(__APPLE__) || defined(AVAILABLE_MAC_OS_X_VERSION_10_12_AND_LATER)
struct timespec ti;
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &ti);
t = (uint32_t)ti.tv_sec * 1000;
t += ti.tv_nsec / 1000000;
#else
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
t = (uint32_t)tv.tv_sec * 1000;
t += tv.tv_usec / 1000;
#endif
return t;
}
int MinHeapTimer::AddTimer(uint32_t expire, TimerHandler cb) {
int64_t timeout = current_time() + expire;
TimerNode* node = new TimerNode;
int id = Count();
node->id = id;
node->expire = timeout;
node->cb = cb;
node->idx = (int)_heap.size();
_heap.push_back(node);
_shiftUp((int)_heap.size() - 1);
_map.insert(make_pair(id, node));
return id;
}
bool MinHeapTimer::DelTimer(int id)
{
auto iter = _map.find(id);
if (iter == _map.end())
return false;
_delNode(iter->second);
return true;
}
void MinHeapTimer::_delNode(TimerNode *node)
{
int last = (int)_heap.size() - 1;
int idx = node->idx;
if (idx != last) {
std::swap(_heap[idx], _heap[last]);
_heap[idx]->idx = idx;
if (!_shiftDown(idx)) {
_shiftUp(idx);
}
}
_heap.pop_back();
_map.erase(node->id);
delete node;
}
void MinHeapTimer::ExpireTimer()
{
if (_heap.empty()) return;
uint32_t now = current_time();
do {
TimerNode* node = _heap.front();
if (now < node->expire)
break;
for (int i = 0; i < _heap.size(); i++)
std::cout << "touch idx: " << _heap[i]->idx
<< " id: " << _heap[i]->id << " expire: "
<< _heap[i]->expire << std::endl;
if (node->cb) {
node->cb(node);
}
_delNode(node);
} while(!_heap.empty());
}
bool MinHeapTimer::_shiftDown(int pos){
int last = (int)_heap.size()-1;
int idx = pos;
for (;;) {
int left = 2 * idx + 1;
if ((left >= last) || (left < 0)) {
break;
}
int min = left; // left child
int right = left + 1;
if (right < last && !_lessThan(left, right)) {
min = right; // right child
}
if (!_lessThan(min, idx)) {
break;
}
std::swap(_heap[idx], _heap[min]);
_heap[idx]->idx = idx;
_heap[min]->idx = min;
idx = min;
}
return idx > pos;
}
void MinHeapTimer::_shiftUp(int pos)
{
for (;;) {
int parent = (pos - 1) / 2; // parent node
if (parent == pos || !_lessThan(pos, parent)) {
break;
}
std::swap(_heap[parent], _heap[pos]);
_heap[parent]->idx = parent;
_heap[pos]->idx = pos;
pos = parent;
}
}
void print_hello(TimerNode *te) {
std::cout << "hello world time = " << te->idx << "\t" << te->id << std::endl;
}
int main() {
MinHeapTimer mht;
mht.AddTimer(0, print_hello);
mht.AddTimer(1000, print_hello);
mht.AddTimer(7000, print_hello);
mht.AddTimer(2000, print_hello);
mht.AddTimer(9000, print_hello);
mht.AddTimer(10000, print_hello);
mht.AddTimer(6000, print_hello);
mht.AddTimer(3000, print_hello);
for (;;) {
mht.ExpireTimer();
usleep(10000);
}
return 0;
}
思路与红黑树的大致相同,不做赘述
单层时间轮:
与最小堆不同,我们这里需要使用静态数组,宏定义数组大小即可,最长定时时间10秒,单位时间1秒,所以使用大于10的数组大小。
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#if defined(__APPLE__)
#include <AvailabilityMacros.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <mach/task.h>
#include <mach/mach.h>
#else
#include <time.h>
#endif
#define MAX_TIMER ((1<<17)-1)
#define MAX_CONN ((1<<16)-1)
typedef struct conn_node { //也可以考虑添加callback
uint8_t used;
int id;
} conn_node_t;
typedef struct timer_node { //定时器节点
struct timer_node *next;
struct conn_node *node;
uint32_t idx;
} timer_node_t;
static timer_node_t timer_nodes[MAX_TIMER] = {0}; //所有定时器节点存储
static conn_node_t conn_nodes[MAX_CONN] = {0};//所有连接节点存储
static uint32_t t_iter = 0; //创建过的定时器节点数目
static uint32_t c_iter = 0;//创建过的连接节点数目
timer_node_t * get_timer_node() { // 注意:没有检测定时任务数超过 MAX_TIMER 的情况!!!
t_iter++;
while (timer_nodes[t_iter & MAX_TIMER].idx > 0) {
t_iter++; //这个定时器节点正在被使用,换下一个试试
}
timer_nodes[t_iter].idx = t_iter;
return &timer_nodes[t_iter];
}
conn_node_t * get_conn_node() { // 注意:没有检测连接数超过 MAX_CONN 的情况
c_iter++;
while (conn_nodes[c_iter & MAX_CONN].used > 0) {
c_iter++;//这个连接节点正在被使用,换下一个试试
}
return &conn_nodes[c_iter];
}
#define TW_SIZE 16
#define EXPIRE 10
#define TW_MASK (TW_SIZE - 1)
static uint32_t tick = 0;
typedef struct link_list {
timer_node_t head;
timer_node_t *tail;
}link_list_t;
void add_conn(link_list_t *tw, conn_node_t *cnode, int delay) {
link_list_t *list = &tw[(tick+EXPIRE+delay) & TW_MASK];
timer_node_t * tnode = get_timer_node();
cnode->used++;
tnode->node = cnode;
list->tail->next = tnode;
list->tail = tnode;
tnode->next = NULL;
} //尾插,因为先到的定时任务需要先访问,比较严谨
void link_clear(link_list_t *list) {
list->head.next = NULL;
list->tail = &(list->head);
}
void check_conn(link_list_t *tw) {
int32_t itick = tick; //获取当前时间戳
tick++;//全局时间戳加一
link_list_t *list = &tw[itick & TW_MASK];// 获取当前时间戳对应的定时器链表,对其进行检查
timer_node_t *current = list->head.next;//定时器链表的头并不是一个实际的定时器节点,所以获取head的next,这是第一个实际的定时器节点
while (current) {
timer_node_t * temp = current;
current = current->next; //下一个
conn_node_t *cn = temp->node; //从定时器节点中拿到对应的连接
cn->used--; //连接的引用计数减一
temp->idx = 0;//该定时器可以回收留待下次使用
if (cn->used == 0) { //引用计数为0,说明连接失活,可以做相应处理
printf("fd:%d kill down\n", cn->id);
temp->next = NULL;
continue;
}
printf("fd:%d used:%d\n", cn->id, cn->used);
}
link_clear(list);//检查完这一时间戳的事件就可以删除了,等待下一次继续添加
}
static time_t
current_time() {
time_t t;
#if !defined(__APPLE__) || defined(AVAILABLE_MAC_OS_X_VERSION_10_12_AND_LATER)
struct timespec ti;
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &ti);
t = (time_t)ti.tv_sec;
#else
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
t = (time_t)tv.tv_sec;
#endif
return t;
}
int main() {
memset(timer_nodes, 0, MAX_TIMER * sizeof(timer_node_t));
memset(conn_nodes, 0, MAX_CONN * sizeof(conn_node_t));
// init link list
link_list_t tw[TW_SIZE];
memset(tw, 0, TW_SIZE * sizeof(link_list_t));
for (int i = 0; i < TW_SIZE; i++) {
link_clear(&tw[i]);
}
// 该测试起始时间为0秒,所以 delay 不能添加超过10的数。
{
conn_node_t *node = get_conn_node();
node->id = 10001;
add_conn(tw, node, 0);
add_conn(tw, node, 5);
}
{
conn_node_t *node = get_conn_node();
node->id = 10002;
add_conn(tw, node, 0);
}
{
conn_node_t *node = get_conn_node();
node->id = 10003;
add_conn(tw, node, 3);
}
time_t start = current_time();
for (;;) {
time_t now = current_time();
if (now - start > 0) {
for (int i=0; i<now-start; i++) //循环保证单位时间移动(1秒走一格)
check_conn(tw);
start = now;
printf("check conn tick:%d\n", tick);
}
usleep(20000);
}
return 0;
}
static timer_node_t timer_nodes[MAX_TIMER] = {0}; //所有定时器节点存储
static conn_node_t conn_nodes[MAX_CONN] = {0};//所有连接节点存储
创建节点存储数组可以做到节点的回收利用,减少节点的创建和删除,静态数组连续存储,访问时间快
#define TW_SIZE 16 时间轮大小
#define EXPIRE 10 定时时间
#define TW_MASK (TW_SIZE - 1) 用于轮转的掩码
static uint32_t tick = 0; 时间戳,指示当前位置
add_conn(link_list_t *tw, conn_node_t *cnode, int delay)
可以设置delay,根据提供的conn_node_t初始化定时任务,并放入tw中正确位置:(tick+EXPIRE+delay) & TW_MASK
link_clear(link_list_t *list)清空一个时间戳上的整个定时器链表
check_conn(link_list_t *tw) 检查当前时间戳对应定时器链表的连接,并对齐引用计数减一,引用计数为0可以做相应处理(回调函数中可以关闭conn,或者给一个信号到管理连接的线程等等)
多层时间轮:
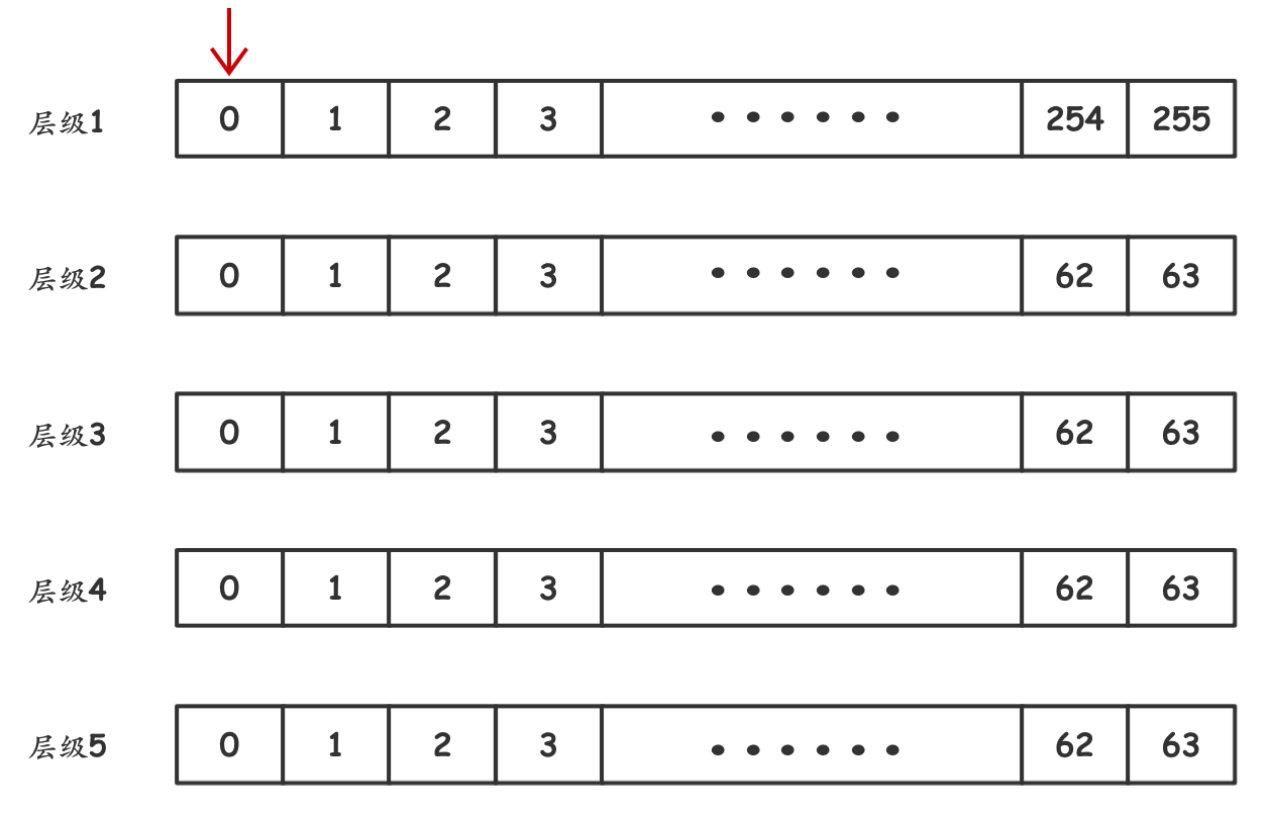
多层时间轮就是在单层的基础上添加几个粒度更大的层,我们只在粒度最小的层上运行定时器(粒度最小的层运行与单层时间轮一样)即可,用钟表举例:最小层运行一周代表秒针转一圈也就是需要转分针了,这时就从第二层上映射下一分钟的所有定时任务到最小层上,第二层每一分钟的任务同时也需要前移(只要移动指针就可以,不用移动所有任务链表),前移操作很容易理解,但映射需要说一下。举例:
我们有一个定时任务是在1分27秒后触发,模拟时钟,第一层的数组大小为60,代表60秒,第二层也是60代表60分钟,第三层24。假设此时tick(时间戳)为0,我们需要将这个定时任务放置于第二层的第0号位置(这里先不区分粒度),并在任务内保存准确的expire时间(1分27),当第一层60秒转完后,我们就需要开始映射,将第二层0号位置上的一串定时任务遍历,一个一个根据其保存的expire时间对60秒取余获得其应该在第一层的位置(27秒对应26号位置),映射到第一层上的26号位置(串到26号下面的链表中)。在下一轮的第一层运转中就会触发定时任务啦。同理,第三层(时针)到第二层(分针)的映射也是相同,使用mask取出定时任务的分位(比如1小时32分15秒就是取出32分,对应第二层的31号位置),找到对应位置放到对应链表中去。
写的代码的时间轮结构如图:
这里所有层级的位数加起来刚好是32位,最低层级使用2的8次方,后续四层都为2的四次方,这样的设计正好用完一个unsigned INT数,在使用mask的时候十分方便。最低层级粒度为10ms。
这里直接附上代码,自行阅读即可:
头文件
#ifndef _MARK_TIMEWHEEL_
#define _MARK_TIMEWHEEL_
#include <stdint.h>
#define TIME_NEAR_SHIFT 8
#define TIME_NEAR (1 << TIME_NEAR_SHIFT)
#define TIME_LEVEL_SHIFT 6
#define TIME_LEVEL (1 << TIME_LEVEL_SHIFT)
#define TIME_NEAR_MASK (TIME_NEAR-1)
#define TIME_LEVEL_MASK (TIME_LEVEL-1)
typedef struct timer_node timer_node_t;
typedef void (*handler_pt) (struct timer_node *node);
struct timer_node {
struct timer_node *next;
uint32_t expire;//过期时间(非定时时间)
handler_pt callback;
uint8_t cancel; //由于idx很多且不断变化很难找到特定节点,通过设计cancel成员来在触发时取消触发操作
int id; // 此时携带参数
};
timer_node_t* add_timer(int time, handler_pt func, int threadid);
void expire_timer(void);
void del_timer(timer_node_t* node);
void init_timer(void);
void clear_timer();
#endif
主文件
#include "spinlock.h"
#include "timewheel.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#if defined(__APPLE__)
#include <AvailabilityMacros.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <mach/task.h>
#include <mach/mach.h>
#else
#include <time.h>
#endif
typedef struct link_list {
timer_node_t head;
timer_node_t *tail;
}link_list_t;
typedef struct timer {
link_list_t near[TIME_NEAR];
link_list_t t[4][TIME_LEVEL];
struct spinlock lock;
uint32_t time;
uint64_t current;
uint64_t current_point;
}s_timer_t;
static s_timer_t * TI = NULL;
timer_node_t *
link_clear(link_list_t *list) {
timer_node_t * ret = list->head.next;
list->head.next = 0;
list->tail = &(list->head);
return ret;
}
void
link(link_list_t *list, timer_node_t *node) {
list->tail->next = node;
list->tail = node;
node->next=0;
}
void
add_node(s_timer_t *T, timer_node_t *node) {
uint32_t time=node->expire;
uint32_t current_time=T->time;
uint32_t msec = time - current_time;
if (msec < TIME_NEAR) { //[0, 0x100)
link(&T->near[time&TIME_NEAR_MASK],node);
} else if (msec < (1 << (TIME_NEAR_SHIFT+TIME_LEVEL_SHIFT))) {//[0x100, 0x4000)
link(&T->t[0][((time>>TIME_NEAR_SHIFT) & TIME_LEVEL_MASK)],node);
} else if (msec < (1 << (TIME_NEAR_SHIFT+2*TIME_LEVEL_SHIFT))) {//[0x4000, 0x100000)
link(&T->t[1][((time>>(TIME_NEAR_SHIFT + TIME_LEVEL_SHIFT)) & TIME_LEVEL_MASK)],node);
} else if (msec < (1 << (TIME_NEAR_SHIFT+3*TIME_LEVEL_SHIFT))) {//[0x100000, 0x4000000)
link(&T->t[2][((time>>(TIME_NEAR_SHIFT + 2*TIME_LEVEL_SHIFT)) & TIME_LEVEL_MASK)],node);
} else {//[0x4000000, 0xffffffff]
link(&T->t[3][((time>>(TIME_NEAR_SHIFT + 3*TIME_LEVEL_SHIFT)) & TIME_LEVEL_MASK)],node);
}
}
timer_node_t*
add_timer(int time, handler_pt func, int threadid) {
timer_node_t *node = (timer_node_t *)malloc(sizeof(*node));
spinlock_lock(&TI->lock);
node->expire = time+TI->time;// 每10ms加1 0
node->callback = func;
node->id = threadid;
if (time <= 0) {
node->callback(node);
free(node);
spinlock_unlock(&TI->lock);
return NULL;
}
add_node(TI, node);
spinlock_unlock(&TI->lock);
return node;
}
void
move_list(s_timer_t *T, int level, int idx) {
timer_node_t *current = link_clear(&T->t[level][idx]);
while (current) {
timer_node_t *temp=current->next;
add_node(T,current);
current=temp;
}
}
void
timer_shift(s_timer_t *T) {
int mask = TIME_NEAR;
uint32_t ct = ++T->time;
if (ct == 0) {
move_list(T, 3, 0);
} else {
// ct / 256
uint32_t time = ct >> TIME_NEAR_SHIFT;
int i=0;
// ct % 256 == 0
while ((ct & (mask-1))==0) {
int idx=time & TIME_LEVEL_MASK;
if (idx!=0) {
move_list(T, i, idx);
break;
}
mask <<= TIME_LEVEL_SHIFT;
time >>= TIME_LEVEL_SHIFT;
++i;
}
}
}
void
dispatch_list(timer_node_t *current) {
do {
timer_node_t * temp = current;
current=current->next;
if (temp->cancel == 0)
temp->callback(temp);
free(temp);
} while (current);
}
void
timer_execute(s_timer_t *T) {
int idx = T->time & TIME_NEAR_MASK;
while (T->near[idx].head.next) {
timer_node_t *current = link_clear(&T->near[idx]);
spinlock_unlock(&T->lock);
dispatch_list(current);
spinlock_lock(&T->lock);
}
}
void
timer_update(s_timer_t *T) {
spinlock_lock(&T->lock);
timer_execute(T);
timer_shift(T);
timer_execute(T);
spinlock_unlock(&T->lock);
}
void
del_timer(timer_node_t *node) {
node->cancel = 1;
}
s_timer_t *
timer_create_timer() {
s_timer_t *r=(s_timer_t *)malloc(sizeof(s_timer_t));
memset(r,0,sizeof(*r));
int i,j;
for (i=0;i<TIME_NEAR;i++) {
link_clear(&r->near[i]);
}
for (i=0;i<4;i++) {
for (j=0;j<TIME_LEVEL;j++) {
link_clear(&r->t[i][j]);
}
}
spinlock_init(&r->lock);
r->current = 0;
return r;
}
uint64_t
gettime() {
uint64_t t;
#if !defined(__APPLE__) || defined(AVAILABLE_MAC_OS_X_VERSION_10_12_AND_LATER)
struct timespec ti;
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &ti);
t = (uint64_t)ti.tv_sec * 100;
t += ti.tv_nsec / 10000000;
#else
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
t = (uint64_t)tv.tv_sec * 100;
t += tv.tv_usec / 10000;
#endif
return t;
}
void
expire_timer(void) {
uint64_t cp = gettime();
if (cp != TI->current_point) {
uint32_t diff = (uint32_t)(cp - TI->current_point);
TI->current_point = cp;
int i;
for (i=0; i<diff; i++) {
timer_update(TI);
}
}
}
void
init_timer(void) {
TI = timer_create_timer();
TI->current_point = gettime();
}
void
clear_timer() {
int i,j;
for (i=0;i<TIME_NEAR;i++) {
link_list_t * list = &TI->near[i];
timer_node_t* current = list->head.next;
while(current) {
timer_node_t * temp = current;
current = current->next;
free(temp);
}
link_clear(&TI->near[i]);
}
for (i=0;i<4;i++) {
for (j=0;j<TIME_LEVEL;j++) {
link_list_t * list = &TI->t[i][j];
timer_node_t* current = list->head.next;
while (current) {
timer_node_t * temp = current;
current = current->next;
free(temp);
}
link_clear(&TI->t[i][j]);
}
}
}